Relays are essential components in various electrical and automation systems, serving as electrically operated switches that allow one circuit to control another. They are widely used in fields such as industrial automation, telecommunications, and even in the automotive industry. Relay comparison refers to the process of evaluating and contrasting the performance and characteristics of different types of relays to determine which one best meets the requirements of a given application. This article will explore the importance of relay comparison, the factors to consider, and how it affects system efficiency and reliability.
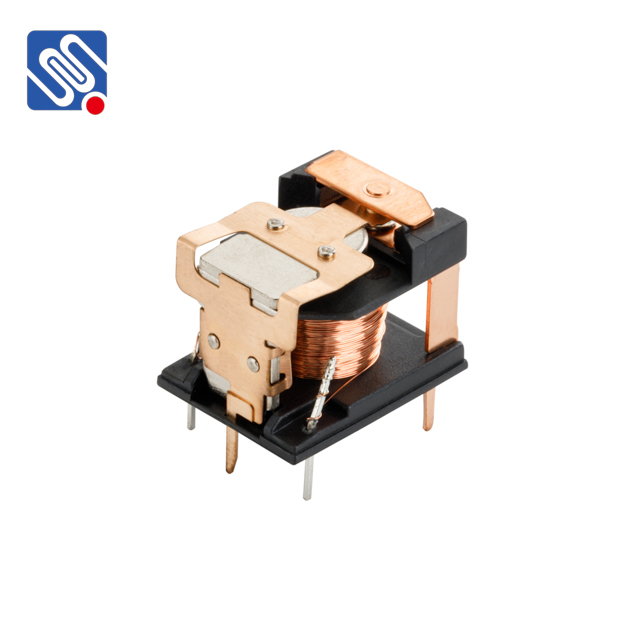
Types of Relays and Their Applications Before diving into the comparison of different relays, it’s important to understand the types of relays commonly used in various industries. Some of the most common types include: Electromechanical Relays (EMR): These relays use mechanical parts, including a coil, armature, and contacts, to switch circuits. They are versatile and can handle both high and low-power circuits. However, they have physical moving parts, which can wear out over time, leading to mechanical failure. Solid-State Relays (SSR): Unlike EMRs, solid-state relays operate without any moving parts, using semiconductor components to switch electrical circuits. SSRS are more durable, have faster switching speeds, and are quieter compared to mechanical relays. However, they often come at a higher cost and can generate more heat.