Relays are integral components in electrical circuits, widely used for their ability to control the flow of electricity based on an input signal. Whether for switching, protection, or automation purposes, understanding the various types of relays and their characteristics is essential for selecting the most suitable relay for a given application. This article will explore the key factors in relay comparison, discussing the differences between types, features, and their ideal applications.
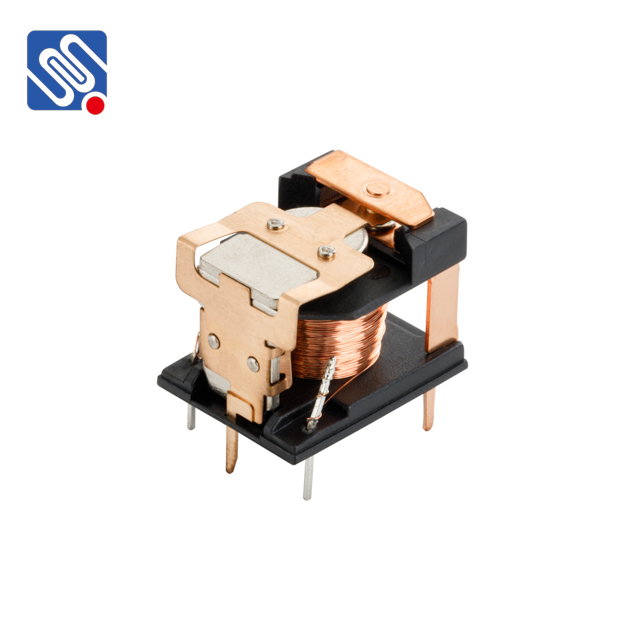
Types of Relays Electromagnetic Relays (EMR) Electromagnetic relays are among the most common types of relays, consisting of a coil, an armature, and contacts. When an electrical current flows through the coil, it generates a magnetic field that attracts the armature, causing the contacts to either open or close, depending on the relay’s design. Electromagnetic relays are versatile and used in a wide range of applications, from controlling motors to circuit protection. Advantages: Simple design and easy to control. Available in various sizes and configurations. Can handle high current and voltage ratings.