A relay circuit is a fundamental component in electrical and electronic systems, serving as a bridge between low-power control signals and high-power devices. Essentially, a relay is an electrically operated switch that uses an electromagnet to mechanically operate a set of contacts. This simple yet powerful principle allows small electrical currents to control much larger currents, making relay circuits indispensable in automation, protection systems, and signal control.
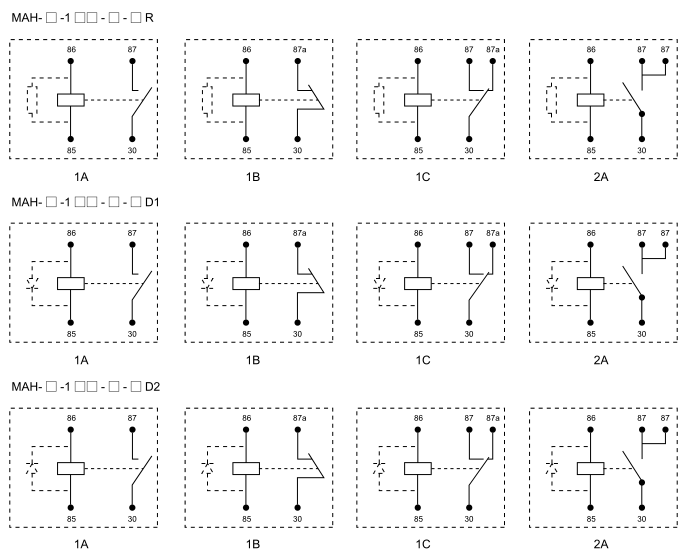
The basic structure of a relay circuit consists of three main parts: the coil, the armature, and the contacts. The coil, when energized by a control voltage, generates a magnetic field that attracts the movable armature. This movement changes the state of the contacts, either closing or opening them depending on their normal configuration. Typically, relays feature normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC) contacts. In a normally open configuration, the contacts remain open when the coil is not energized, while in a normally closed configuration, they remain closed until the coil is powered. This flexibility allows engineers to design circuits that respond differently under specific conditions.