A Relay electrical diagram is a crucial component in understanding how relay systems work in electrical circuits. Relays are widely used in electrical engineering to control high-power circuits using low-power control signals. They are essentially electromagnetic switches that can open or close circuits based on electrical input. This makes them essential in a variety of applications, including automotive systems, industrial machinery, telecommunications, and even household appliances. In this article, we will break down the essential elements of a relay electrical diagram and how it operates in practical scenarios.
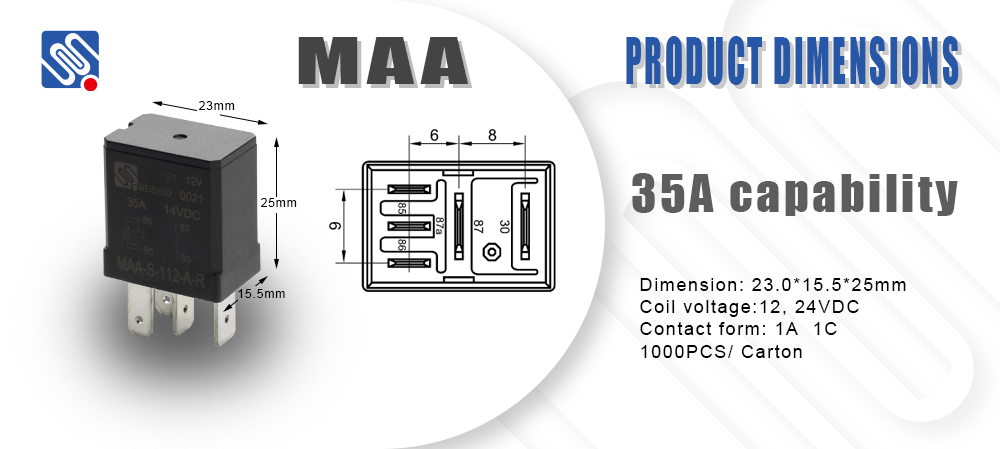
What is a Relay? A relay is an electrically operated switch. It is made up of a coil of wire, an electromagnet, and one or more sets of contacts that can be opened or closed. The coil is energized by a control signal, which produces a magnetic field that moves the contacts. When the relay coil is energized, it allows current to flow through the connected circuit, thus controlling a load that could otherwise be too large for a direct switch. Relays are often used to control a circuit by a low-power signal, where the relay provides a pathway for a much higher power to pass through. In other words, they are used to switch large amounts of current with a small control signal.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.